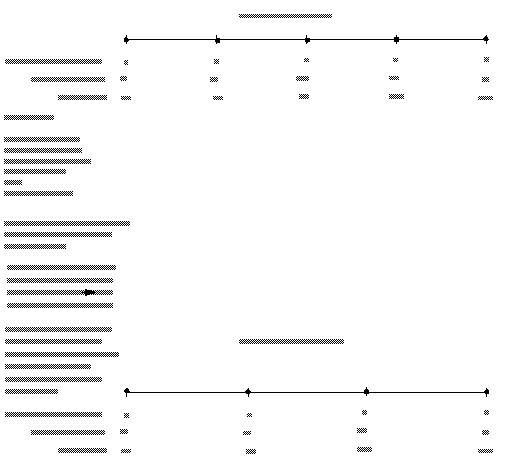
resample a uniform field to reduce (or increase) its size
group DVdownsize_unif {
Mesh_Unif+Node_Data+Iparam &in {
xform+nonotify;
nnodes+req;
};
float+Iparam factor[in.ndim];
Mesh_Unif+Node_Data+Oparam out{
&xform<weight=-1> => in.xform;
};
method+notify_val+notify_inst upd_downsize = "downsize";
} ;
DVdownsize_unif resamples a uniform field (mesh type Mesh_Unif) using a scaling factor. Where the factor is > 1, DVdownsize_unif reduces the size of the field, saving processing time and memory by "thinning out" the data. Where factor < 1, DVdownsize_unif increases the size of the field by duplicating data.
DVdownsize_unif works like this (see the 1D example on the following page):
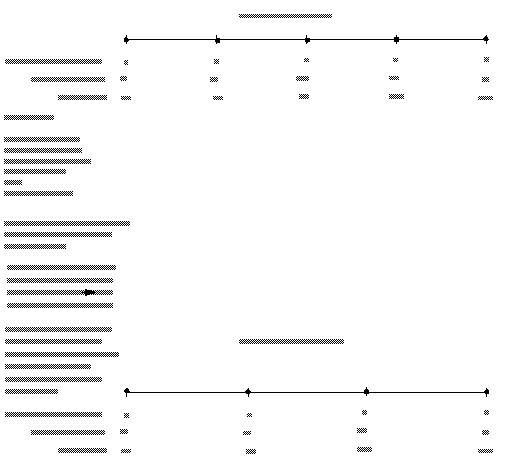
For each dimension i (X, Y, and Z) calculate:
• dims_out[i] = dims_in[i] / factor[i]
•
Round dims_out up or down to the nearest whole integer.
Note: the two endpoints are always preserved in the output data.
Note: the extents of the input field are preserved in the output field.
• Calculate the ratio of the intervals between nodes dims_in : dims_out
• For each new array index, find the nearest whole integer by rounding up or down.
• Use the node data and coordinates in the input field that are found by these index values as the node data and coordinates for the output field.
Note: Throughout the process, the actual node data values and coordinate values are irrelevant. All that is being manipulated are the indexes into these arrays.
A reference to an input field containing a Mesh_Unif and Node_Data.
A float array used as a scaling coefficient. The output field's values (and coordinates for irregular data) are:
dims_out[i] = dims_in[i] / factor [i]
where i cycles through the dims of the field, either 1D, 2D, or 3D.
The length of the factor array (1D: just X; 2D: X and Y; 3D: X, Y and Z) is taken from the ndim of the Grid_Struct. You control the factor for each dimension separately.
Note: factors < 1 will make the output field larger. For example, a factor of 0.5 will double the size of the output field.
The output is a new object that contains a new Mesh_Unif. The new Mesh_Unif's points array (extents) will occupy the same "space" as the input field's Mesh_Unif.
The output field also contains a new Node_Data object containing the data associated with the downsized region.