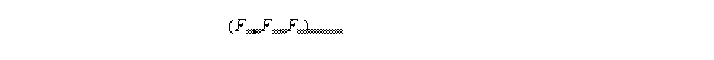
Synopsis
compute the divergence of a vector field
Input Ports
|
in_field |
Mesh + Node_Data |
|
ui_parent |
user interface parent object |
Parameters
|
data component |
UIradioBoxLabel |
select a component of the input field |
Output Ports
|
out_fld |
same Mesh + Node_Data |
|
out_obj |
output renderable object |
Description
divergence computes the divergence of a vector field with any mesh type.
Input Ports
in_field
The input must be a field with any type of mesh and Node_Data. At least one of the Node_Data's components must be a three-element vector.
ui_parent
A port to connect to a user interface object that contains the macro's widgets. By default, it is connected to the default user interface object in the application in which the macro is instanced. (This default connection is not drawn.)
Parameters
data component
UIradioBoxLabel. A set of radio buttons to pick which component of in_field to use to compute the divergence. You must pick a three-element vector component. The default is the first (0th) component. If node data labels are present, they are displayed.
Output Ports
out_fld
The output field contains a new Node_Data that has a scalar float value at each node representing the divergence. Its mesh is a reference to the input mesh.
out_obj
This is a renderable version of the output field.
Algorithm
The algorithm that computes the divergence in structured meshes is a finite difference approximation based on a central difference scheme. For unstructured meshes, the function is based on the cell shape functions and their derivatives.
In both cases, where the vector node data component is:
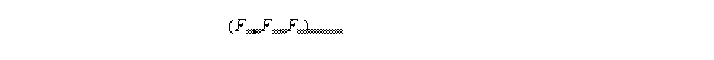
The equation used to compute the divergence is:
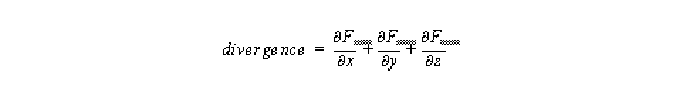
Example
Libraries.Examples.Vizualization.Div
examples/div.v
File
v/modules.v
See also